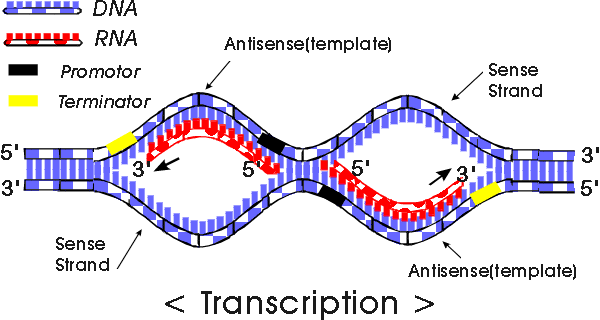
Transcription is also carried out in a 5' - 3' direction.
It is also important to note that only one strand of DNA will be required in the process of transcription.
7.3.2 Distinguish between the sense and antisense strands in DNA
Sense strand is not transcribed into RNA, its sequence will be the "DNA version" of the mRNA sequence.
Antisense strand is transcribed into the RNA, its sequence will be the "DNA version" of the tRNA anticodon sequence
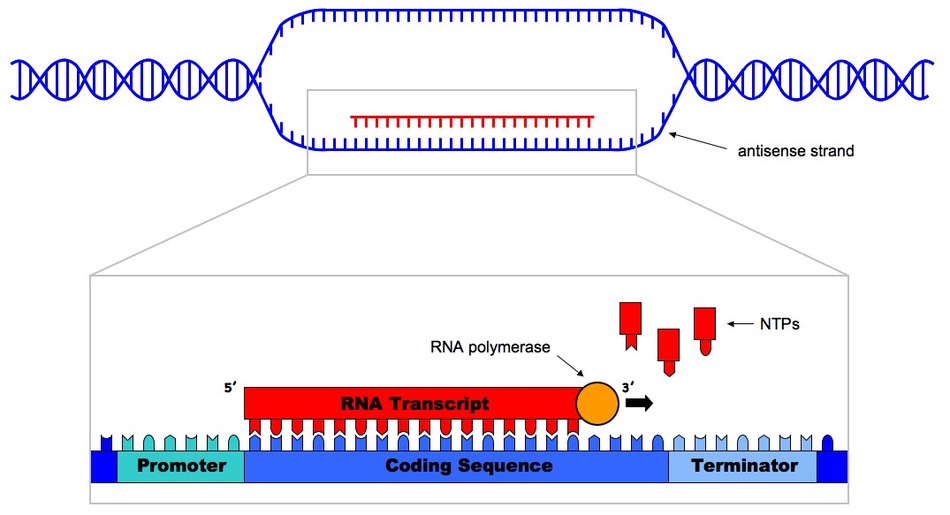
7.3.3 Explain the process in transcription in prokaryotes, including the role of the promoter region, RNA polymerase, nucleoside triphosphate and the terminator
This is what transcription should look like.
The promoter is responsible for the initiation of transcription (in prokaryotes, a number of genes may be regulated by a single promoter). While the terminator is responsible for terminating the transcription. However this differs between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Process
- RNA binds to the promoter region
- Initiates transcription
- RNA polymerase uncoils the DNA
- Only one strand is used, the anti-sense strand
- Free nucleoside triphosphate bond to their complementary bases on the anti-sense strand
- Uracil replaces Thymine
- As the nucleoside triphosphates bind, they become nucleotides and release energy to form the phosphodiester bond by losing the two phosphate groups
- The mRNA is built in a 5' - 3' direction
- RNA polymerase forms covalent bonds between the nucleotides and keeps moving along the DNA until it reaches the terminator
- The terminator signals the RNA polymerase to stop transcription
- RNA polymerase is released and the mRNA separates from the DNA
- DNA rewinds
7.3.4 State that eukaryotic RNA needs the removal of introns to form mature mRNA
Pre-mRNA has been produced through transcription of the anti-sense strand as described for prokaryotic transcription.
Introns are broken down in the nucleus and the remaining exons are called the mature mRNA. Which is then exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm for translation into a polypeptide



沒有留言:
張貼留言