7.2.1 State that DNA replication occurs in a 5' to 3' direction
DNA replication is a semi-conservative process, this means that a new strand is synthesised from an original template strand. The free nucleotide 5' end is bonded covalently to the 3' end which is on the already formed polynucleotide.
The 5C joins with the 3C, hence 5' to 3'.
7.2.2 Explain the process of DNA replication in prokaryotes, including the role of enzyme (helicase, DNA polymerase, RNA primase and DNA ligase), Okazaki fragments and deoxynucleoside triphosphates.
Helicase unwinds and separates the double stranded DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. This occurs at specific regions creating a replication fork of two polynucleotide strand in anti-parallel direction.
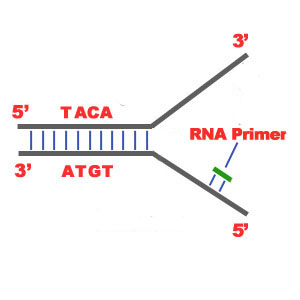
RNA primase synthesises a short RNA primer on each template strand to provide an attachment and initiation point for polymerase III
DNA polymerase III adds deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs) to the 3' end of the polynucleotide chain, synthesizing in a 5' - 3' direction
The dNTPs pair up with their complementary base pairs and the two additional phosphate releases energy to form a phosphodiester bond. This process continues smoothly on the leading strand (5' - 3') while not so smoothly on the lagging strand (3' - 5')
The lagging strand forms Okazaki fragments. This is because the the dNTPs must join from the direction of 5' - 3', thus the DNA polymerase III must work backwards towards the origin.
DNA polymerase I removes the RNA primers and replaces them with DNA.
DNA ligase joins the okazaki fragments together to form a continuous strand.
7.2.3 State that DNA replication is initiated at many points in a eukaryotic chromosomes
Eukaryotic genomes are typically larger than prokaryotic genomes, DNA replication is initiated at many points simultaneously in order to limit the time required for DNA replication to occur.
It is mainly used to get the work done faster.






沒有留言:
張貼留言