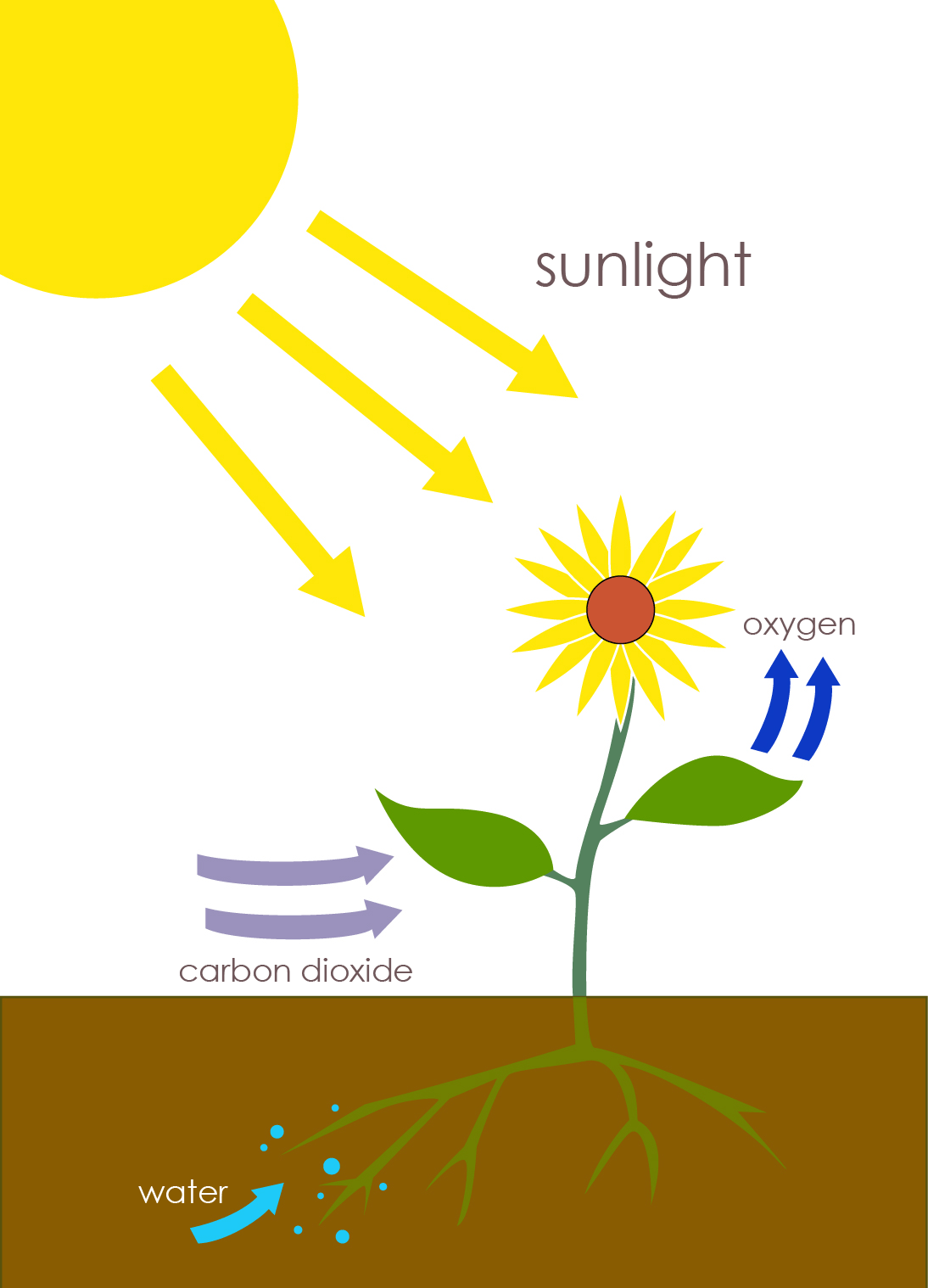
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants synthesis organic compounds (e.g glucose) from inorganic compounds (carbon dioxide and oxygen) in the presence of sunlight
3.8.2 State that light from the Sun is composed of a range of wavelengths (colours).
Light from the sunlight is made up of all the colours of the electro-magnetic spectrum
3.8.3 State that chlorophyll is the main photosynthetic pigment
Chlorophyll is the main site of light absorption in the light dependent stage of photosynthesis. There are a different number of chlorophyll molecule, each with their own distinct absorption spectra.
3.8.4 Outline the differences in absorption of red, blue and green light by the chlorophyll
This is a graph that shows the light absorption spectra
The main colour of light that is absorbed are red and blue. Green is the colour that is mainly reflected. Thus the green colour we can see from the chloroplast. During the winter times, trees produce less chlorophyll as there are less sunlight. Thus the change in colour of leaves during the different season
3.8.5 State that light energy is used to produce ATP, and to split water molecules (photolysis) to form oxygen and hydrogen.
Photosynthesis consists of two reactions; light dependent and light independent.
Light Dependent
- Light is absorbed by the chlorophyll molecules (green) inside the chloroplast
- The light energy from the photons (light) is transferred to excite the electrons thus changing the energy from light to chemical
- The chemical energy is used to produce ATP
- Light energy also splits the water molecule in a process called photolysis, producing oxygen and hydrogen
- The hydrogen is taken up by the hydrogen carrier (NADP+) to form NADPH
- The splitting of water also releases electrons which replaces the loss of electrons in the chloroplast
- The products of these two reaction are then taken to the light independent reaction
3.8.6 State that ATP and hydrogen (derived from the photolysis of water) are used to fix carbon dioxide to make organic molecules.
The second part of photosynthesis uses the products from the light dependent reaction
- ATP and hydrogen carriers are the products of the light dependent reaction
- They are used to fix the carbon molecules together, adding carbon dioxide to an organic compound.
- This allows for more complex organic molecules (e.g. sugars)
- The organic molecules are then used in cellular respiration or stored as starch.
3.8.7 Explain that the rate of photosynthesis can be measured directly by the production of oxygen or the uptake of carbon dioxide, or indirectly by an increase in biomass
The rate of photosynthesis can be measured by the production of oxygen, the uptake of carbon dioxide or the increase in biomass. But water can't be used as a measure because it is also used in other process.
Measuring carbon dioxide uptake
- Carbon dioxide uptake can be measured by placing a plant in an enclosed space with water
- Carbon dioxide interacts with the water molecules, producing bicarbonate and hydrogen ions. This increases the acidity of the solution
- The change in pH can be used to measure the uptake by a plant (More carbon dioxide = More alkaline solution)
Measuring oxygen production
- Oxygen production can be measure by submerging a plant in an enclosed space with water attached to a sealed gas syringe
- Any production of water will change the meniscus of the sealed gas syringe
Measuring change in biomass
- To measure glucose production, the change of biomass could be measured
- The plant is required to be completely dehydrated to ensure the change in biomass reflects a change in organic matter and not water intake.
- Or measure the change in starch content in a plant. This could be quantitative data by using a colorimeter.
3.8.8 Outline the effects of temperature, light intensity and carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis.
Rate of photosynthesis:
Photosynthesis is a biological reaction which also requires the assistance of enzymes. Temperature will increase the rate of reaction by increasing the chances of reaction happening. However, once it reaches (c), the enzymes will denature and the reaction will no longer be able to take place.
The effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis. As carbon dioxide is one of the reactants in the reaction, an increase of concentration will increase the probability of the reaction taking place. However the curve will converge as there will be another limiting factor.
Light is an important element required in photosynthesis. An increase in the light intensity will increase the rate of reaction. However the curve will start to converge as there will be a limiting factor which stops the rate of reaction from increasing.










沒有留言:
張貼留言