Compounds containing carbon that are found in living organisms are called organic compounds.
The exceptions are the gas carbon dioxide, hydrogen carbonates and mineral calcium carbonate.
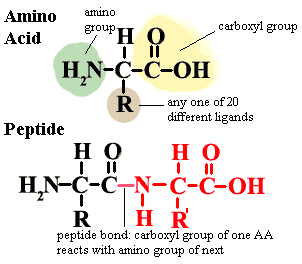
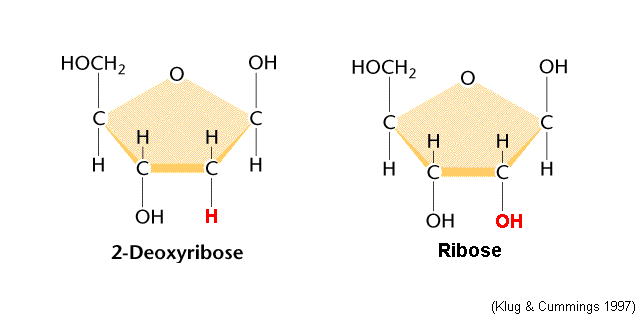
3.2.2 Identify amino acids, glucose, ribose and fatty acids from diagrams showing their structure.
3.2.3 List three examples each of monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides
Glucose
Galactose
Fructose
Disaccharides
Lactose
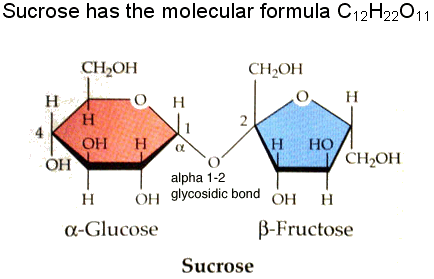
Sucrose
Maltose
Polysaccharides
Glycogen
Starch
Cellulose
3.2.4 State one function of glucose, lactose and glycogen in animals, and of fructose, sucrose and cellulose in plants.
Monosaccharides-
Glucose - (Animals and Plants) used for cellular respiration
Galactose - (Animals) Used for production of milk
Fructose - (Plants) Used in the production of sucrose
Disaccharides-
Lactose - (Animals) (Glucose + Galactose) Produced in mammary glands
Sucrose - (Plants) (Glucose + Fructose) Produced in green leaves
Maltose - (Plants) (Glucose + Glucose) Breakdown product in the hydrolysis of starch
Polysaccharides-
Glycogen - (Animals) Storage carbohydrates, stored in the liver and other cells
Starch - (Plants) Storage for carbohydrates
Cellulose - (Plants) Bundle of fibres as the main component of the cell walls.
3.2.5 Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides.
Condensation Reaction: (Water is formed; similar to "condensation")
Hydrolysis Reaction: (Water is broken down; "lysis" refers to breaking down)
Monosaccharides forming a disaccharide: (Glycosidic Bond)
Fatty acids and Glycerol forming triglycerides: (Ester Bond)
Amino acids forming a polypeptide: (Peptide Bond)
3.2.6 State three functions of lipids
Structure: Phospholipids in the cell membrane allows for the cell to maintain its shape
Heat Insulation: A layer of fat under the skin to reduce heat loss
Buoyancy: Lipids are less dense than water, this allows animals to float
Energy Storage: Stores energy in the form of fat.
3.2.7 Compare the use of carbohydrates and lipids in energy storage.
Similarities:
- Complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides) and lipids both contain a lot of chemical energy and be used for energy storage
- Complex carbohydrates and lipids are both insoluble in water
- Carbohydrates and lipids both burn cleaner than proteins (They do not yield nitrogenous gas)
Differences:
- Lipids molecules contain more energy per gram than carbohydrates (2x)
- Carbohydrates are more readily digested than lipids and release their energy more rapidly
- Monosaccharides and disaccharides are water-soluble and easier to transport
- Animals tend to use carbohydrates primarily for short-term storage, while lipids are used more for long-term energy storage
- Carbohydrates are stored as glycogen in animals while lipids is stored in fat.






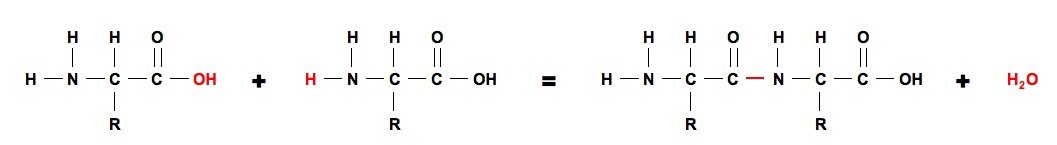


沒有留言:
張貼留言